Java Classes And Objects
Java is an object-oriented programming language.
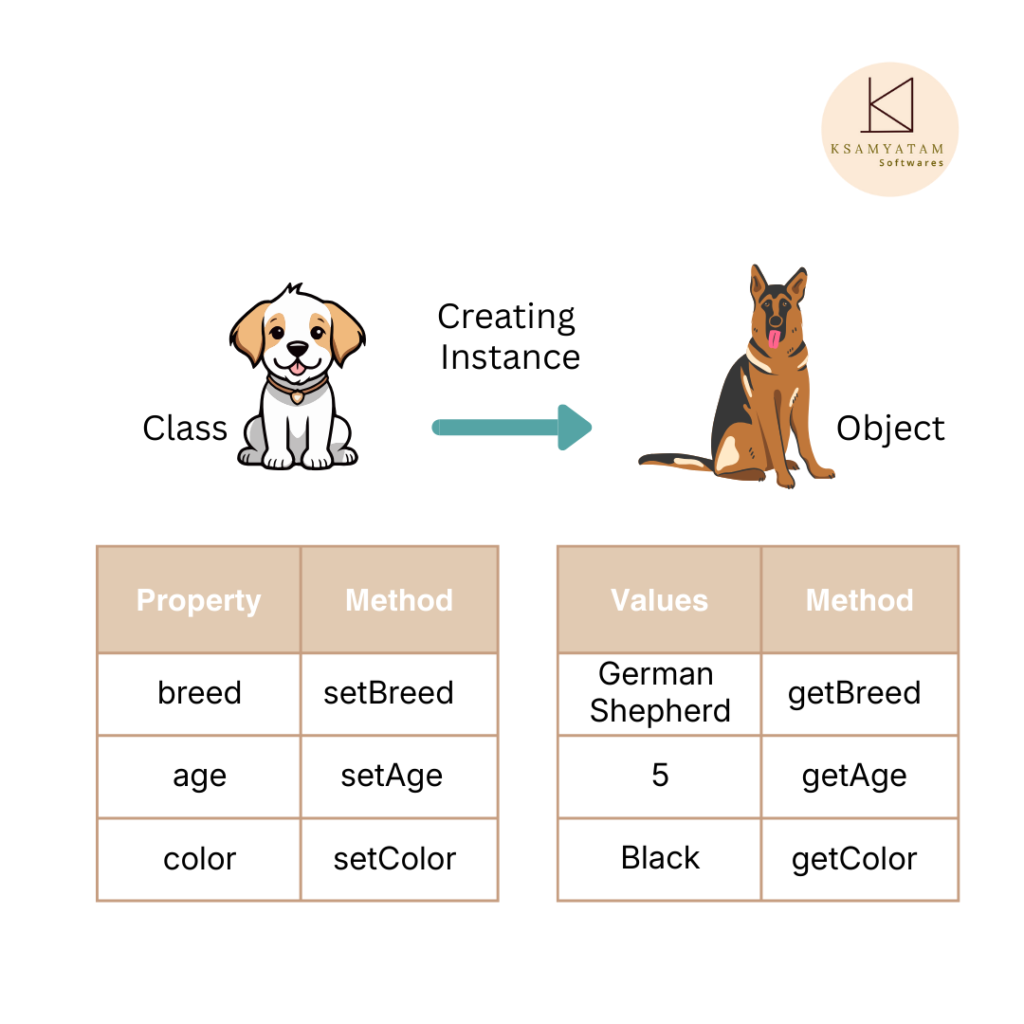
In Java, classes and objects are the foundation model and fundamental building blocks of Object-Oriented Programming (OOP). A class is a blueprint for creating objects, that share common properties and behavior and provide initial values for member variables and implementations of behaviors (methods). An object is an instance of a class, representing a specific entity with a defined state and behavior form from the class template.
Java Class :
A Java class is a blueprint that defines data and behavior for objects. It groups related fields and methods in a single unit. Memory for each class member is allocated only when an object is created.Each class has its methods and attributes that can be accessed and manipulated through the objects.
Properties of Java Class
- Java Class follows all of the properties of OOPs such as inheritance, encapsulation, abstraction, etc.
- Java Class contains mainly two components : Methods and Data Members.
- Java Class is a blueprint for creating objects having common properties and behaviour.
- Java Class can also be a nested class.
- Java Class does not take any byte of memory.
Types of Java Class Variables
Local variables :
- Local variables are declared within a method, constructor, or a specific block of code (e.g., inside a loop or an if statement).
- Local variables are only accessible within the block in which they are declared.
- Local variables are created when the method or block is entered and are destroyed when the method or block finishes execution.
- Local variables do not have a default value; they must be explicitly initialized before use, or the compiler will throw an error.
- Local variables are typically stored in the stack memory
Example :
public void myMethod() {
int count = 10; // 'count' is a local variable
if (count > 5) {
String message = "Hello"; // 'message' is local to the if block
System.out.println(message);
}
// Cannot access 'message' here, it is out of scope
}Instance (Non-Static) variables :
- Instance variables are declared within a class but outside of any method, constructor, or block.They belong to an instance (object) of the class.
- Instance variables are accessible by all methods, constructors, and blocks within the class.
- Instance variables are created when an object of the class is instantiated using the new keyword and destroyed when the object is garbage-collected.
- If not explicitly initialized, Java assigns a default value (e.g., 0 for numeric types, false for booleans, and null for object references)
- Instance variables are stored in the heap memory.
- Each object maintains its own unique copy of the instance variables.
Example :
public class Car {
String brand; // Instance variable
int year; // Instance variable
public Car(String brand, int year) {
this.brand = brand;
this.year = year;
}
}Class (Static) variables :
- Static variables, or class variables, are declared within a class, outside any method, constructor, or block, using the static keyword.
- Static variables can be accessed from anywhere within the class, and by external code using the class name.
- Static variables are created when the class is loaded into memory, which happens only once, and they exist for the entire duration of program execution.
- Similar to instance variables, Static variables are assigned default values if not explicitly initialized.
- Static variables are stored in a special area of memory known as static memory (part of the heap).
- There is only one single copy of a static variable, shared by all instances (objects) of the class. They are often used for constants (e.g., public static final double PI = 3.14;)
Example :
public class Counter {
static int count = 0; // Static variable shared by all instances
public Counter() {
count++; // Incremented every time an object is created
}
}Java Object :
A Java object is an instance of a class. It is created using the new keyword followed by the class constructor and has its data and operations. All the objects have a state and a behavior.For example, a dog has its own state like name, breed, and color, and the behavior like barking,wagging the tail, and running.
Declaring A Java Object :
There are three steps when creating an object from a class :
- Declaration : A variable declaration with a variable name with an object type.
- Instantiation : The ‘new’ keyword is used to create the object.
- Initialization : The ‘new’ keyword is followed by a call to a constructor. This call initializes the new object.
Syntax :
Class_name object_name = new Class_name([parameters]);Java Program For Class And Object :
// Dog.class
// Creating a Java class
public class Dog {
// Declaration and Initialization
String breed;
int age;
String color;
// Methods
public void setBreed(String breed) {
this.breed = breed;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
// Method to print values
public void dogDisplay() {
System.out.println("Dog Details :");
System.out.println(this.breed);
System.out.println(this.age);
System.out.println(this.color);
}
}
// DogPrintValue.class
public class DogPrintValue {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating Java Object For Class Dog
Dog obj = new Dog();
// Properties
obj.setBreed("German Shepherd");
obj.setAge(5);
obj.setColor("Black");
// Print all values
obj.dogDisplay();
}
}Output :
Dog Details :
German Shepherd
5
BlackJava Program For Class And Object (Getter And Setter) :
//Creating a Java class
public class Dog {
// Declaration and Initialization
String breed;
int age;
String color;
public String getBreed() {
return breed;
}
public void setBreed(String breed) {
this.breed = breed;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dog [breed=" + breed + ", age=" + age + ", color=" + color + "]";
}
}
// DogSetterGetter.class
public class DogSetterGetter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating Java Object For Class Dog
Dog obj = new Dog();
// Properties
obj.setBreed("German Sheperd");
obj.setAge(5);
obj.setColor("Black");
// Print all values
System.out.println(obj.getBreed());
System.out.println(obj.getAge());
System.out.println(obj.getColor());
System.out.println(obj.toString());
}
}Output :
German Sheperd
5
Black
Dog [breed=German Sheperd, age=5, color=Black]